Introduction
Kubernetes (K8s) is a powerful tool for container orchestration, but effective resource management can be a challenge. Poor resource management can lead to performance bottlenecks, application failures, and increased costs. In this post, we will explore four common resource management issues in Kubernetes: noisy neighbors, CPU throttling and limits, Out of Memory (OOM) issues with limits, and OOM issues on loaded nodes. We’ll provide clear explanations and practical examples to help you manage these issues effectively.
1. Noisy Neighbors: The Silent Performance Killer
How to Mitigate Noisy Neighbors
- Resource Requests and Limits: Set resource requests to ensure a minimum amount of resources for each pod and limits to cap the maximum resources a pod can use.
- Node Affinity and Taints/Tolerations: Use these Kubernetes features to control pod placement and isolate high-resource pods from others.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: high-resource-pod
spec:
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: high-resource
operator: In
values:
- "true"
containers:
- name: example-container
image: example-image
resources:
requests:
memory: "512Mi"
cpu: "1000m"
limits:
memory: "1024Mi"
cpu: "2000m"
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Node
metadata:
name: example-node
labels:
high-resource: "true"2. CPU Throttling and Limits: Striking the Right Balance
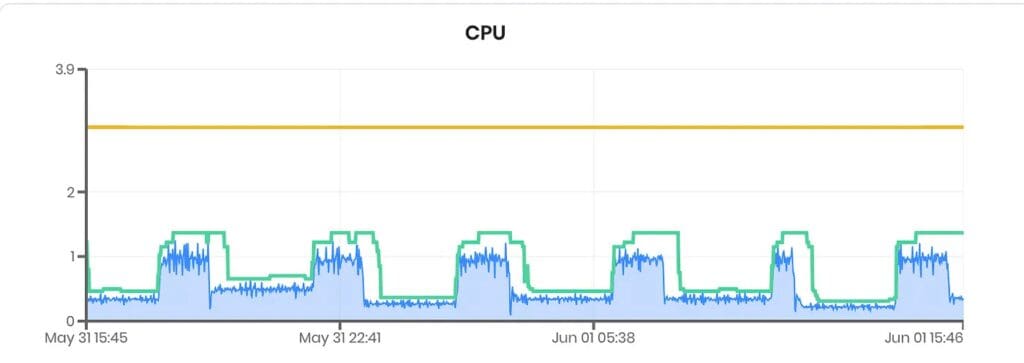
What Is CPU Throttling?
CPU throttling occurs when a pod exceeds its allocated CPU limit, causing Kubernetes to restrict its CPU usage. This can lead to performance degradation and latency issues.
Example
Consider an application that processes real-time data. If the CPU limit is set too low, the application might not process data quickly enough, resulting in delays and potentially lost data.
How to Avoid CPU Throttling
- Set Appropriate Limits: Understand your application’s CPU requirements and set limits that allow for peak usage.
- Use a Vertical Pod Autoscaler: a Vertical Pod Autoscaler can automatically adjust the CPU and memory requests/limits of your pods based on actual usage. You can use the community VPA or a full-blown autoscaling platform like ScaleOps
3. OOMs and Limits: Preventing Memory Shortages
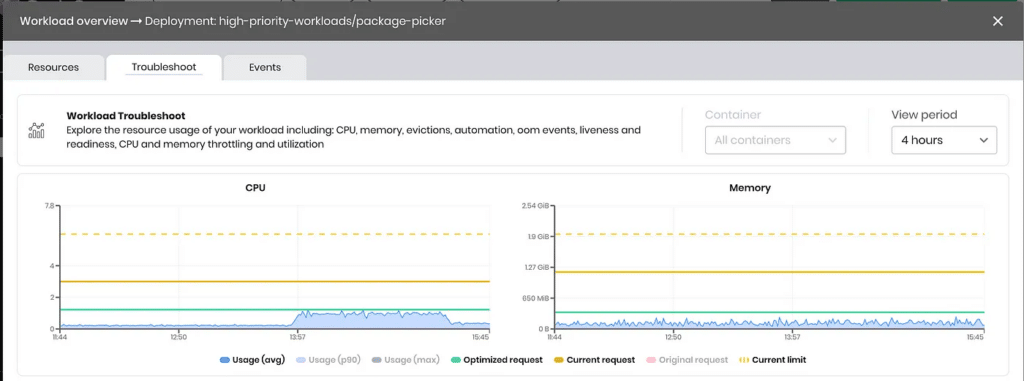
What Are OOMs?
Out of Memory (OOM) issues occur when a pod tries to use more memory than is available, causing the kernel to terminate the process. This can lead to application crashes and data loss.
Example
A Java application with a high memory footprint might crash if its memory limit is set too low, leading to an OOM error.
How to Prevent OOMs
- Set Memory Requests and Limits: Ensure pods have enough memory to operate without exceeding node capacity.
- Monitor Memory Usage: Use tools like Prometheus and Grafana to monitor memory usage and adjust limits as necessary.
4. OOMs and Loaded Nodes: Balancing Resource Allocation
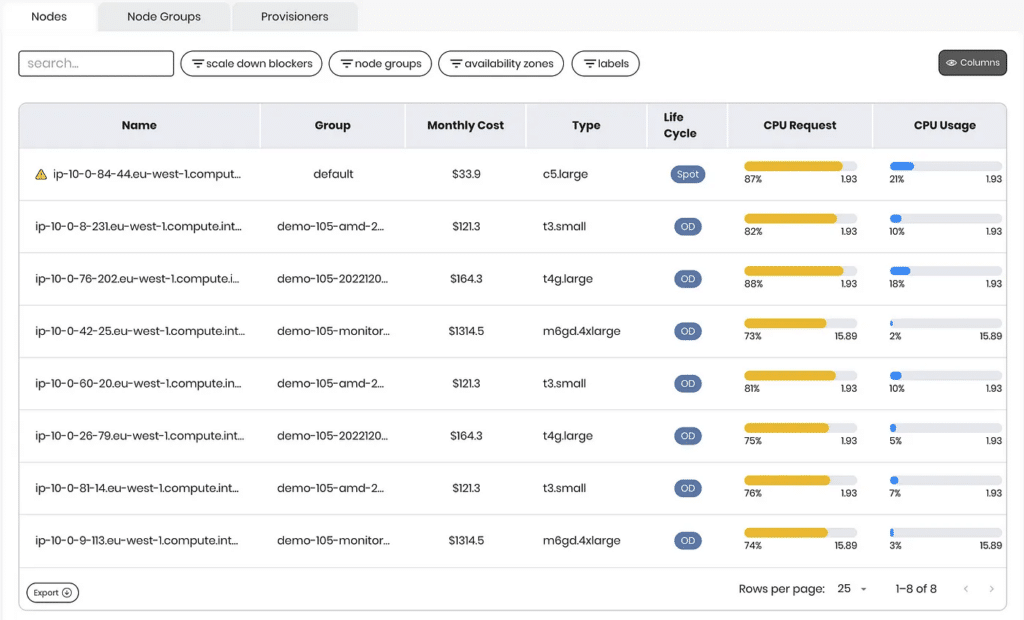
What Happens on Loaded Nodes?
When a node is heavily loaded, even pods with adequate memory limits might face OOM issues if the total memory usage exceeds the node’s capacity. This is particularly problematic in environments with dynamic workloads.
Example
Consider a cluster running multiple applications with varying memory usage patterns. If several applications peak in memory usage simultaneously, the node might run out of memory, causing OOM errors across multiple pods.
How to Manage Loaded Nodes
- Rightsize Resource Requests: Ensure that resource requests accurately reflect the memory needs of your pods, helping to prevent nodes from being overloaded.
- Constantly Monitor Node Capacity and Utilization
Conclusion
Effective resource management is crucial for maintaining the performance and reliability of your Kubernetes applications. Using ScaleOps you can ensure that your applications run smoothly and efficiently by understanding and addressing issues like noisy neighbors, CPU throttling, OOM errors, and loaded nodes. Automating resource requests and limits will help you manage resources effectively and prevent common pitfalls.
Ready to take your Kubernetes cluster to the next level? Visit ScaleOps to discover advanced solutions for optimizing your cloud infrastructure.