As organizations increasingly adopt Kubernetes for container orchestration, efficient resource management becomes paramount. Automatic pod rightsizing ensures optimal allocation and cost efficiency. In this post we compare the Kubernetes Vertical Pod Autoscaler (VPA) with ScaleOps and explain why ScaleOps is the stronger choice for production-grade, automated, real-time pod rightsizing.
Key takeaways
- Zero Downtime: ScaleOps uses smart rollout strategies to prevent service interruptions, whereas VPA typically requires pod restarts.
- Seamless Integration: Unlike VPA, ScaleOps integrates natively with HPA and Keda for dynamic scaling based on real-time metrics.
- Proactive Reliability: ScaleOps features built-in auto-healing for OOM and liveness issues, ensuring higher workload availability.
- Advanced Resource Efficiency: ScaleOps supports sidecars, custom workloads (like Spark), and active bin-packing to maximize cluster utilization.
1. Zero downtime
Only the ScaleOps Platform can change resource requests in production without taking the service offline.
VPA: VPA adjusts resource requests for pods, but it typically requires restarting the pods to apply the new configurations. This can lead to downtime, particularly for single-replica workloads, impacting the application’s availability.
ScaleOps: ScaleOps ensures zero downtime for single-replica workloads by using a smart rollout strategy. It creates a new pod before replacing the old one, allowing for seamless transitions without any service interruptions.
2. HPA integration
VPA:
- Focuses only on vertical scaling based on historical usage.
- Kubernetes documentation is clear: “The VPA cannot be used together with the Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA) targeting CPU or memory.”
- This hard limitation means teams must choose between VPA and HPA or build custom work-arounds.
ScaleOps:
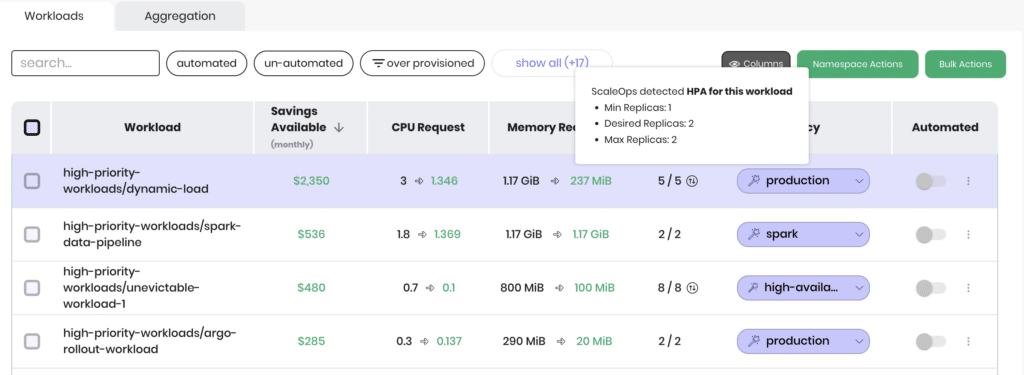
Developers continue using familiar HPA YAML while ScaleOps eliminates drift in the background.
Seamlessly reads existing HPA definitions
No manual coordination is required. The two layers cooperate automatically.
3. Auto Healing
VPA: VPA does not include built-in mechanisms for auto-healing based on real-time events. It focuses on adjusting resource requests and limits based on historical data.
ScaleOps: ScaleOps monitors API-server events like OOMs and liveness issues to take immediate corrective action. This ensures optimal performance by addressing issues as they arise, enhancing the reliability of your workloads.
4. Fast Response Time
VPA: VPA operates based on historical usage patterns, which can result in slower response times to sudden changes in workload demands. This might lead to resource shortages during unexpected usage spikes.
ScaleOps: ScaleOps continuously adapts to changing usage patterns with a fast-reaction mechanism. It monitors live traffic and node state, taking immediate action to adjust resource requests during sudden usage spikes, ensuring consistent performance.
5. Supported Workloads
VPA: VPA works well with workloads managed by native Kubernetes controllers but may require additional configuration for custom workloads or those not natively supported.
ScaleOps automatically detects and optimizes the full spectrum of Kubernetes workload types, including:
- Deployments / StatefulSets – traditional microservices and databases
- Jobs / CronJobs – batch and scheduled processing
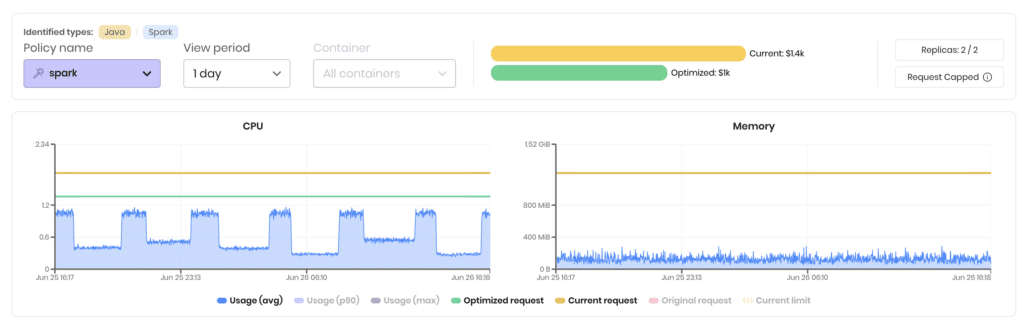
- Spark & other data-processing operators – out-of-the-box policies for driver and executor pods
- Custom controllers & CRDs – any pod not owned by a native controller
This breadth ensures even edge-case services receive the right resources without manual tuning.
6. Sidecar Support
VPA: VPA may struggle with sidecar containers, as it treats them the same as primary containers, potentially leading to race conditions and conflicts during scaling.
ScaleOps: ScaleOps fully supports sidecar containers without any race condition issues or conflicts. This ensures that both primary and sidecar containers are managed effectively, maintaining application stability.
7. Active Bin Packing
VPA: VPA does not focus on active bin-packing of pods with PDB constraints or annotations preventing optimization, which can lead to inefficient resource utilization and higher costs.
ScaleOps: ScaleOps actively bin-packs these unevictable pods, improving resource utilization and cost savings. This proactive approach helps in maintaining an optimal balance of resources across the cluster.
8. Policy-Based Management
VPA: VPA offers basic configuration options but lacks advanced policy-based management for specific workload requirements, limiting customization.
ScaleOps lets teams define granular optimization rules through Kubernetes-native CRDs:
- Percentile targets – e.g., allocate requests to the 95th-percentile of observed usage.
- Look-back windows – choose whether to evaluate the last 30 minutes, 6 hours, or any custom window.
- Guardrails & caps – hard minimum/maximum resources, replica floors, and disruption budgets.
With these levers you can align resource behavior with SLOs, cost goals, or compliance constraints—no code changes required.
Conclusion
While Kubernetes VPA provides a robust solution for vertical pod autoscaling, ScaleOps offers a more comprehensive and dynamic approach to automatic pod rightsizing. With features like zero downtime, seamless HPA integration, auto healing, fast response times, broad workload support, sidecar support, active bin-packing, and policy-based management, ScaleOps stands out as the superior choice.
Ready to optimize your Kubernetes workloads effortlessly? Try ScaleOps today and experience the benefits firsthand.



